Network Optimization Is Key to Your businesses Growth
Unlock your business potential with our expert IT consulting and innovative solutions
Different Categories of Wireless Surveys
Predictive Site Surveys -- is conducted before the deployment of a wireless network. It uses software to simulate the wireless environment and predict the coverage and performance of the network. This type of survey is useful for planning a new wireless network or for optimizing an existing network.
Physical site survey -- is conducted after the deployment of a wireless network. It uses a spectrum analyzer or other wireless survey tool to measure the actual signal strength and interference levels in the environment. This type of survey is useful for troubleshooting wireless problems and for ensuring that the network is meeting its performance goals.
Passive site survey -- is a type of physical site survey that does not connect to the wireless network. It simply measures the signal strength of all the wireless networks in the environment. This type of survey is useful for identifying sources of interference and for determining the best location for access points.
Post validation site survey -- is conducted after changes have been made to a wireless network. It is used to verify that the changes have improved the performance of the network. This type of survey is often used after adding new access points or after changing the configuration of the network.

How would we benefit from a Wi-Fi Survey

Identifying access points that are deployed for the wrong purpose -- An example would be using the incorrect models of AP's in many locations throughout a building. By having devices with omni-directional antenna's and installing the AP's at heights greater than 20FT would significantly reduce signal strength for devices connecting at floor level. Identifying RF cell overlap problems between access points -- Having omni-directional antennas on the AP's, there were too many RF cell overlaps between the AP's. As devices were connecting saw multiple AP's that were using the same channels, the wireless devices essentially had to wait in line to connect to that channel. Identifying a coverage void or null with outdoor AP's -- RF is a line-of-sight technology and having AP's mounted at various heights where the AP's were obstructed by walls, columns and or beams. AP power levels left at the default manufacturers configuration -- When all APs are broadcasting at the same power level, it can create interference with each other. This can lead to decreased performance and connectivity issues for users. By adjusting the power levels of each AP, you can help to reduce interference and improve performance. AP's installed/mounted at troublesome locations -- If an AP is installed in a location where there is a lot of interference from other wireless devices, such as microwaves or cordless phones, it can cause problems with the signal. This can lead to dropped connections, slow speeds, and other performance issues.
What's included with a Wi-Fi Survey
1. An onsite visit with our expert wireless network engineer: (Don't overlook the importance of this, many companies are not capable of providing industry standard testing and expertise)
2. Manual inspection of wireless hardware: Leverage our specialists to solve complex technological problems in various environments, including where your devices are located and mounted.
3. Running wireless analysis software to capture data: From your existing Wi-Fi network, to make sure you have the best Wi-Fi service - both customer & corporate - with access to AirMagnet, kahau and other survey toolsets.
4. Assessment and analysis of data captured, and we will generate a full report document.
Purpose -- Why is the wireless survey being performed? What is the goal? (Often wireless surveys are conducted the determine if the RF coverage shown in a Predictive RF Design matches what's seen during the survey). (Other instances assessments review the current wireless network design and identify sources of ongoing performance problems).Scope -- What's included and what is not?Survey test infrastructure -- What hardware and software tools are being used to measure RF coverage? (For example, The Ekahau Site Survey Pro with the Ekahau NIC-300 USB Wireless adapters and an Aruba IAP-305 access point in survey mode).
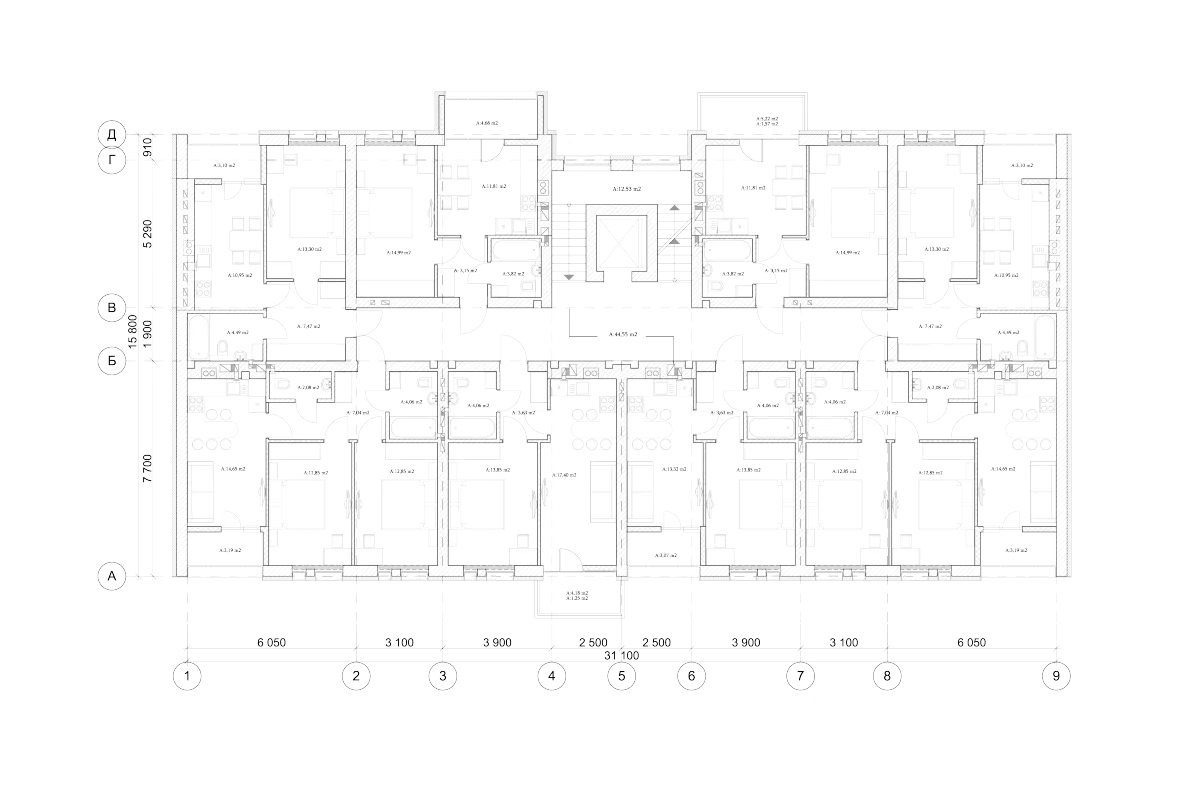
5. The report outlines requirements as follows:
SNR (Signal to noise ratio) minimumSignal strength minimumData rate minimumMinimum number of access points
6. A floor plan listing routes -- for the site survey, and access point locations
7. Coverage and performance narrative: Survey Includes
Data rate heatmap: for 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz wireless frequencies (the highest speed a wireless device can transmit data)Maximum effective throughput heatmap: For 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz wireless frequencies (Due to the current laws of physics RF works in half-duplex mode and true data throughput rate will be approximately half the data rate).RF signal strength/coverage heatmap: For 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz wireless frequencies (the that can offer most basic measure of wireless networking health can often explain problems with unreliable connections and low data throughput.
8. Depending on the type of site survey, other metrics that may be included are:
CCI (co-channel interference) analysis -- This identifies any crosstalk between two different transmitters on the same RF channel.ACI (adjacent channel interference) -- This identifies any extraneous power from a signal on an adjacent RF channel (In most wireless site surveys, a floor plan with access point locations, data rate heatmap, throughput heatmap, and signal strength heatmap is created for each floor in the building/dwelling)

Copyright © 2025 Gagiteck Inc. - All Rights Reserved
Contact Us
813.517.9479
8870 N Himes Ave Ste. 631
Tampa, Florida 33614